
Immunohistochemical Techniques Types
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is a method used in the laboratory to detect specific antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. It’s widely used in clinical and research settings to diagnose diseases and understand the distribution and localization of biomarkers. Here are the primary types of immunohistochemical techniques:
Direct method
Direct method utilizes a primary labeled antibody, which is conjugated to either an enzyme or fluorochrome. The primary antibody attaches directly to the antigen in tissue section or cytological specimens and produce a color or fluorescence. This method is easy and fast although it deficits sensitivity when the amount of antigen in the tissue is low (Fig. 1a).
Indirect method
Indirect methods use a secondary labelled antibody against the non-labelled primary antibody. This method has higher sensitivity rates since more than one secondary antibody can bind to the same primary antibody and thus amplify the signal. Additionally, one secondary antibody can be applied against several primary antibodies that were raised at the same animal (Fig. 2b).
Peroxidase anti-peroxidase (PAP) complex and alkaline phosphatase anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP) complex methods
Peroxidase anti-peroxidase (PAP) complex method is composed of two anti-peroxidase antibodies and three peroxidase molecules. After the conjugation of primary antibody to an antigen, a secondary bridging antibody is added, which binds to the primary antibody. Afterwards, PAP complex is applied, which will also bind to the bridging antibody then signal. This method can also be applied using alkaline phosphatase anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP) complex. This technique may show high background staining, which makes it less popular (Fig. 1d).
Immunogold silver staining (IGSS) method
This method can be applied with direct and indirect techniques. In this method, colloidal gold is used as a label. Afterwards, metallic silver is added, which result in the production of metallic silver precipitate which can be detected using light microscopy. This technique shows higher sensitivity than PAP method however, it shows higher background staining (Fig. 1e).
Streptavidin-biotin complex (ABC) method
Streptavidin-biotin complex (ABC) method is the most used method in immunohistochemistry, and it is composed of three steps. The first step includes the addition of non-labelled primary antibody to tissue section or cytological smear. Secondly, biotin conjugated secondary antibody is added, which binds to the primary antibody. Then, enzyme-labelled streptavidin or enzyme-labelled streptavidin and biotin is added. The most used enzymes are horseradish peroxidase and alkaline phosphatase. They are commonly used with diaminobenzidine (DAB) and aminoethyl carbazole (AEC) as chromogens, respectively (Fig. 1f). This method shows high sensitivity as it depends on the high affinity of streptavidin to biotin. However, dealing with tissue high in endogenous biotin will need subsequent blocking methods.
Each of these techniques has specific advantages and is chosen based on the required sensitivity, specificity, and the nature of the tissue and antigen being studied.
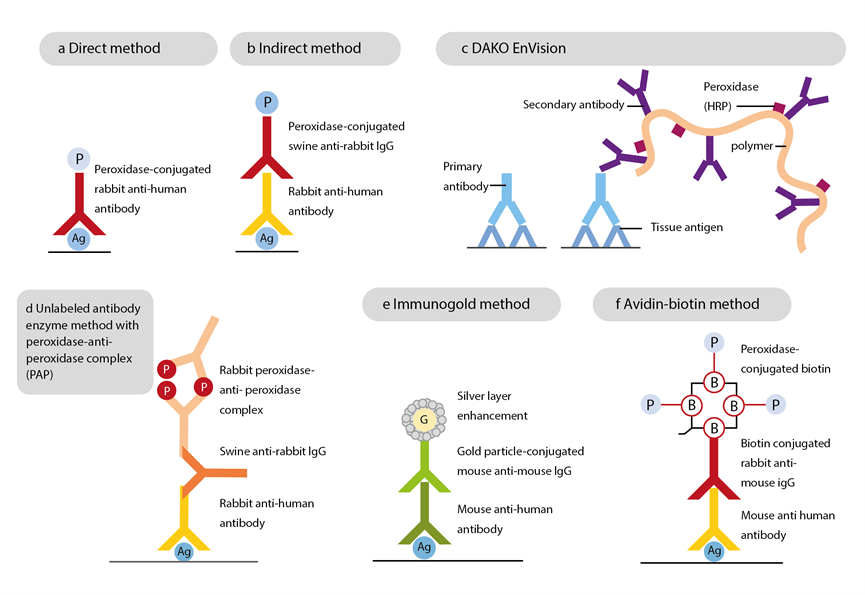
Figure1: Immunohistochemical methods
Prof.Aziza Rashed Alrafiah


Leave a Reply