Congo Red Stain
The Congo Red stain is a histological stain used primarily to identify the presence of amyloid proteins in tissues.
Principle
Congo Red is a diazo dye binding selectively to tissue sections’ amyloid fibrils. The dye has an affinity for the beta-pleated sheet configuration of the amyloid fibrils. When bound to amyloid and viewed under polarized light, Congo Red-stained sections exhibit an apple-green birefringence, a characteristic optical property crucial for the definitive identification of amyloid.
Method of Application
The Congo Red staining method involves several steps:
- Fixation: Tissue samples are fixed, typically with formalin, to preserve structural integrity.
- Deparaffinization and Rehydration: Paraffin-embedded tissue sections are deparaffinized with xylene and rehydrated through a series of graded alcohols to water.
- Staining:
- The tissue sections are stained with a Congo Red solution. The solution is often slightly alkaline, which promotes the binding of the dye to the amyloid fibrils.
- The sections are then rinsed to remove any excess dye.
- Counterstaining (Optional):
- Nuclei may be counterstained with a mild hematoxylin solution to provide a contrast, typically staining the nuclei blue. This step enhances the visualization of tissue architecture and the distribution of amyloid.
- Dehydration and Mounting:
- The sections are dehydrated in alcohol, cleared in xylene, and mounted under a glass coverslip using a resinous mounting medium.
Utilization
Congo Red staining is extensively used in pathology for the following purposes:
- Diagnosis of Amyloidosis: To confirm the presence of amyloid in various tissues such as the kidney, liver, heart, and others. Amyloidosis can be systemic or localized; accurate diagnosis is essential for proper management.
- Research: In studying the pathology of amyloid-related diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, where amyloid plaques are a significant feature.
This staining technique is critical in clinical and research settings because it definitively diagnoses amyloid deposits within tissue sections.


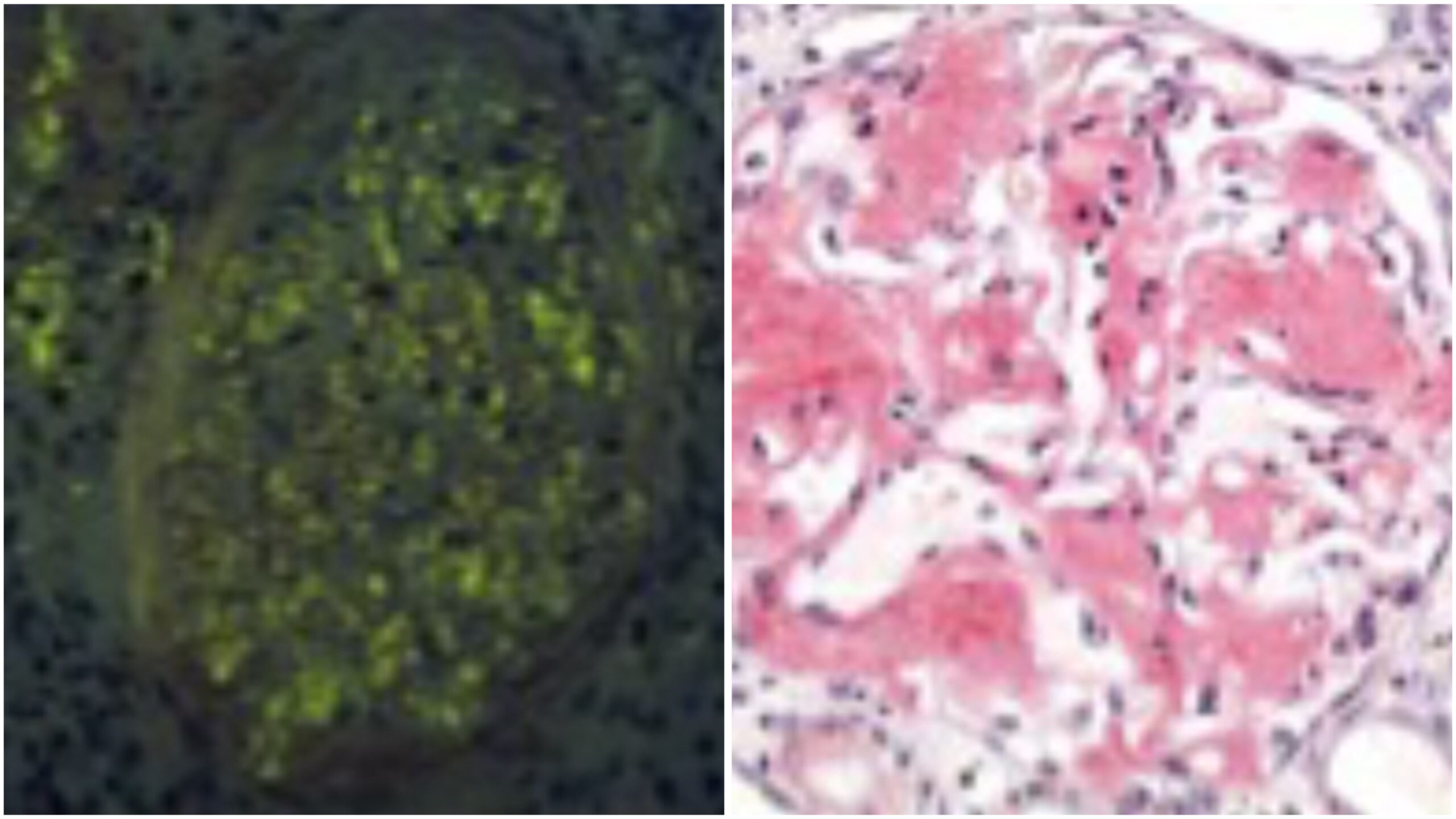
- (A) Amyloidosis in Kidney: This panel shows a kidney tissue section stained with Congo Red, highlighting amyloid deposits in red. The characteristic apple-red coloration of amyloid deposits is visible, indicating areas affected by amyloidosis.
- (B) Amyloidosis in Kidney with Polarizer: The same section exhibits apple-green birefringence when viewed under polarized light. This distinctive optical property confirms the presence of amyloid fibrils, a hallmark of amyloidosis.


Leave a Reply