
Alcian Blue
In tissues, the alcian Blue stain is a versatile histological stain used primarily to visualize acidic polysaccharides, such as glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and mucopolysaccharides.
Principle
Alcian Blue is a basic dye that binds to negatively charged acidic tissue components. It has a high affinity for the sulfate and carboxyl groups in the glycosaminoglycans of the extracellular matrix, mucins, and other connective tissue components. The intensity of the coloration with Alcian Blue reflects the density and distribution of acidic polysaccharides in the tissue.
Method of Utilization
The typical procedure for using Alcian Blue staining in histology involves several steps:
- Fixation: To preserve their structure, tissue samples are fixed, usually with formalin.
- Deparaffinization and Rehydration: If embedded in paraffin, sections are deparaffinized with xylene and rehydrated through graded alcohols to water.
- Staining:
- The tissue sections are stained with Alcian Blue solution. The pH of the staining solution can vary (commonly pH 2.5 or 1.0) depending on the targeted tissue components. pH 2.5 is generally used to stain all types of acid mucins, while pH 1.0 is for more selective staining of sulfated mucins.
- The sections are rinsed in water and then counterstained with another dye, often nuclear fast red or eosin, to provide a contrast, making the blue-colored acidic components stand out against a pink or red background.
- Dehydration and Clearing: Sections are then dehydrated through graded alcohols, cleared in xylene, and mounted under a coverslip with a mounting medium.
Applications
Alcian Blue stain is utilized in various clinical and research settings:
- Pathology: To identify diseases involving mucin-secreting cells, such as mucinous carcinoma or mucopolysaccharidoses.
- Research: Studying the distribution and quantity of glycosaminoglycans in connective tissues can be important in understanding processes such as tumor metastasis, inflammation, and developmental biology.
- Veterinary Pathology: Similar applications to human pathology for examining animal tissues.
Alcian Blue staining is a fundamental histopathological tool for highlighting essential tissue elements indicative of various pathological states or developmental changes.
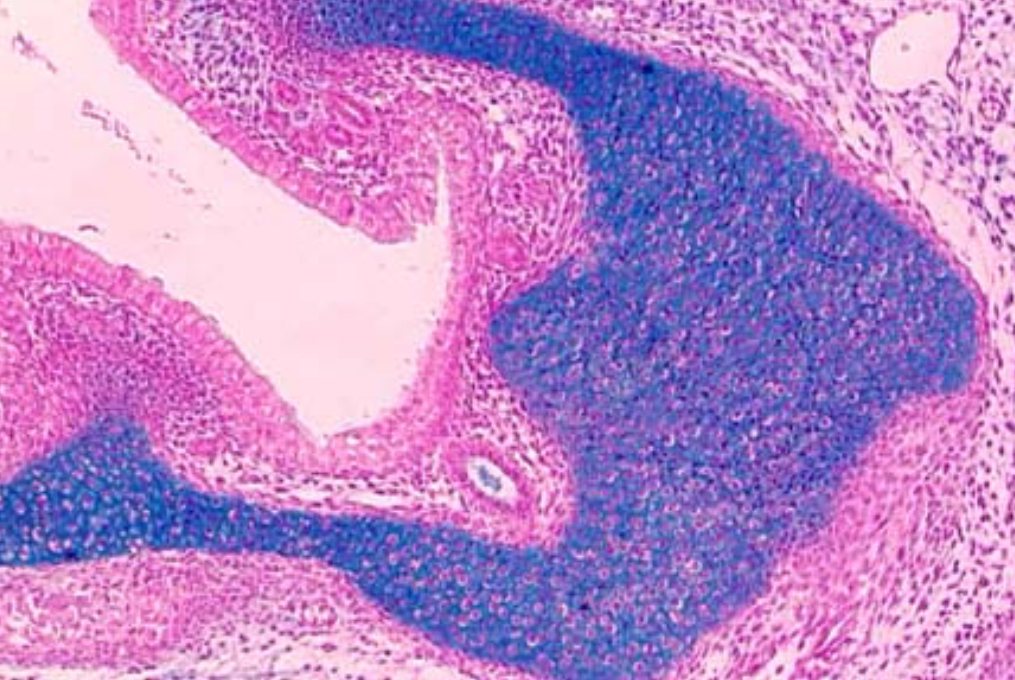
This microscopic view showcases a tissue section stained with Alcian Blue, which specifically binds to acidic polysaccharides, such as glycosaminoglycans, in the connective tissue matrix. The staining process highlights:
- Blue: Areas rich in acidic polysaccharides are stained blue, reflecting their concentration and distribution within the tissue.
- Light Pink Background: A contrasting backdrop enhances the visibility of the blue-stained components, facilitating detailed histological analysis.
Prof. Aziza Rashed Alrafiah


Leave a Reply